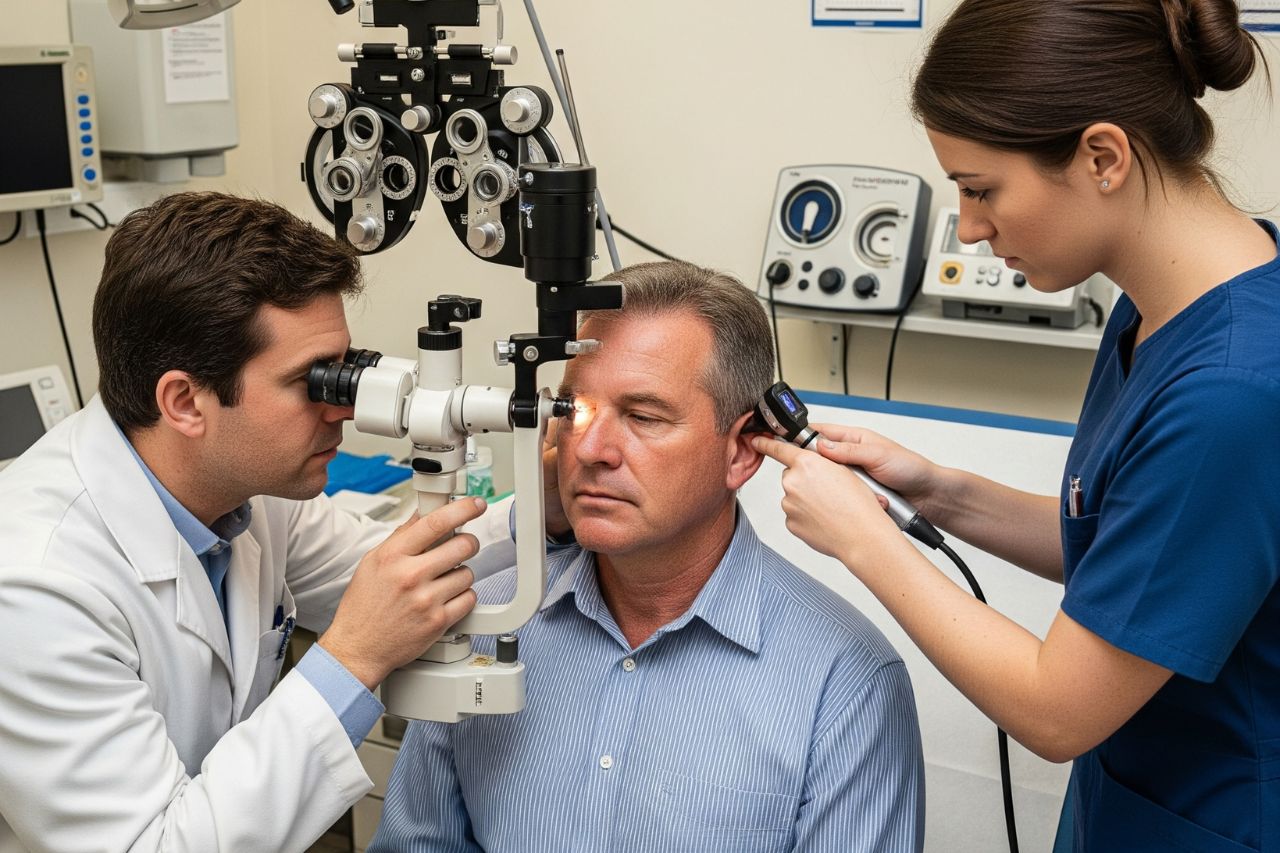
The eye and ear tests are an important component of the GAMCA (now Wafid) medical examination, designed to ensure that applicants have adequate sensory functions to perform their prospective jobs safely and effectively in GCC countries. While generally less extensive than blood tests or X-rays, they are still crucial for overall fitness assessment.
Here’s what’s typically involved in the eye and ear tests:
Eye Tests
The eye examination focuses on visual acuity, colour vision (for certain roles), and the absence of contagious or severe eye conditions.
- Visual Acuity Test (Snellen Chart):
- This is the most common test, where you’ll be asked to read letters or numbers on a chart from a specified distance.
- Purpose: To measure your sharpness of vision.
- Corrective Lenses: If you wear glasses or contact lenses, you’ll likely be tested with and without them. It’s essential to bring your corrective lenses and, if possible, your prescription.
- Requirements: Visual acuity should be suitable for the job. For roles requiring sharp vision, like drivers, the requirement is often strict (e.g., not less than 6/6 or 6/9, with or without glasses).
- Color Vision Test:
- This test assesses your ability to distinguish between different colours. It’s particularly important for jobs where colour recognition is critical for safety or operational reasons (e.g., electricians, pilots).
- Method: Often involves Ishihara plates (circles with coloured dots forming numbers or patterns) or similar tests.
- Field of Vision (Peripheral Vision):
- Some examinations may include a basic check of your peripheral vision to ensure you can see objects within a certain range.
- Screening for Eye Diseases:
- The doctor will visually inspect your eyes for signs of contagious eye diseases such as:
- Granular conjunctivitis
- Purulent conjunctivitis
- Trachoma
- They also look for other severe eye conditions that might require prolonged medical treatment or surgery, like cataracts and glaucoma. The presence of such conditions can lead to an “unfit” status.
- The doctor will visually inspect your eyes for signs of contagious eye diseases such as:
Ear Tests
The ear examination focuses on hearing ability and the absence of ear infections.
- Basic Hearing Test (Audiometry):
- You might undergo a simple hearing test where sounds are played at different frequencies and volumes to determine the softest sounds you can hear.
- Purpose: To assess your overall hearing ability.
- The severity of Hearing Loss: The acceptable level of hearing loss can vary depending on the specific GCC country and the job role. Some jobs may require good hearing in both ears, while others might allow for moderate hearing loss, potentially with the use of hearing aids.
- Examination for Ear Infections:
- The doctor will inspect your ears to ensure you are not suffering from any infections in the middle or inner ear. Chronic or active ear infections can be a reason for an “unfit” declaration.
Important Considerations:
- Job Specificity: The exact requirements for eye and ear tests can vary based on the specific job role you are applying for in the GCC country. Roles demanding higher sensory acuity will have stricter requirements.
- Corrective Devices: If you use corrective lenses or hearing aids, always bring them to your examination along with any relevant prescriptions or documentation. Inform the medical staff about your condition.
- Communication: If you have known vision or hearing impairments, it’s advisable to inform the medical centre beforehand so they can make any necessary accommodations during the examination.
Passing these sensory tests is vital as they contribute to the overall assessment of your fitness to work and reside safely in the GCC countries.



