Those applying for family visas and residency permits in GCC countries (Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, Oman, Kuwait, Bahrain, and Qatar) must take the GAMCA medical exam. Preventing the transmission of infectious diseases and making sure dependents don’t endanger public health are the main objectives.
Here’s a breakdown of the requirements for dependents:
General Requirements for Family Visas:
- Mandatory Test: The GAMCA medical test is a mandatory health assessment for applicants seeking family visas.
- Purpose: It screens for infectious diseases (like HIV/AIDS, Hepatitis B & C, Syphilis, Tuberculosis) and chronic illnesses to ensure public health safety in the GCC countries.
- Process: The process involves a physical examination, laboratory tests (blood and urine), and a chest X-ray.
- Booking: Appointments can be booked online through the official GAMCA/Wafid portal. You will need to fill in passport information, choose your country and a nearby approved medical centre, make an online payment, and then print your GCC slip.
- Documents Required: Original passport and photocopy, recent passport-sized photographs (as per GCC standards, often with a white background), GCC medical slip, visa reference number (if applicable), and payment receipt. Some countries may also require a COVID-19 vaccination certificate and an Aadhaar card.
- Results: Results are typically ready within 24 to 72 hours and can be checked online. A “FIT” report allows the visa process to proceed, while an “UNFIT” report usually leads to visa denial. Reapplication may be possible after a waiting period (3-6 months), depending on the condition and country laws, but serious illnesses like HIV generally do not permit reapplication.
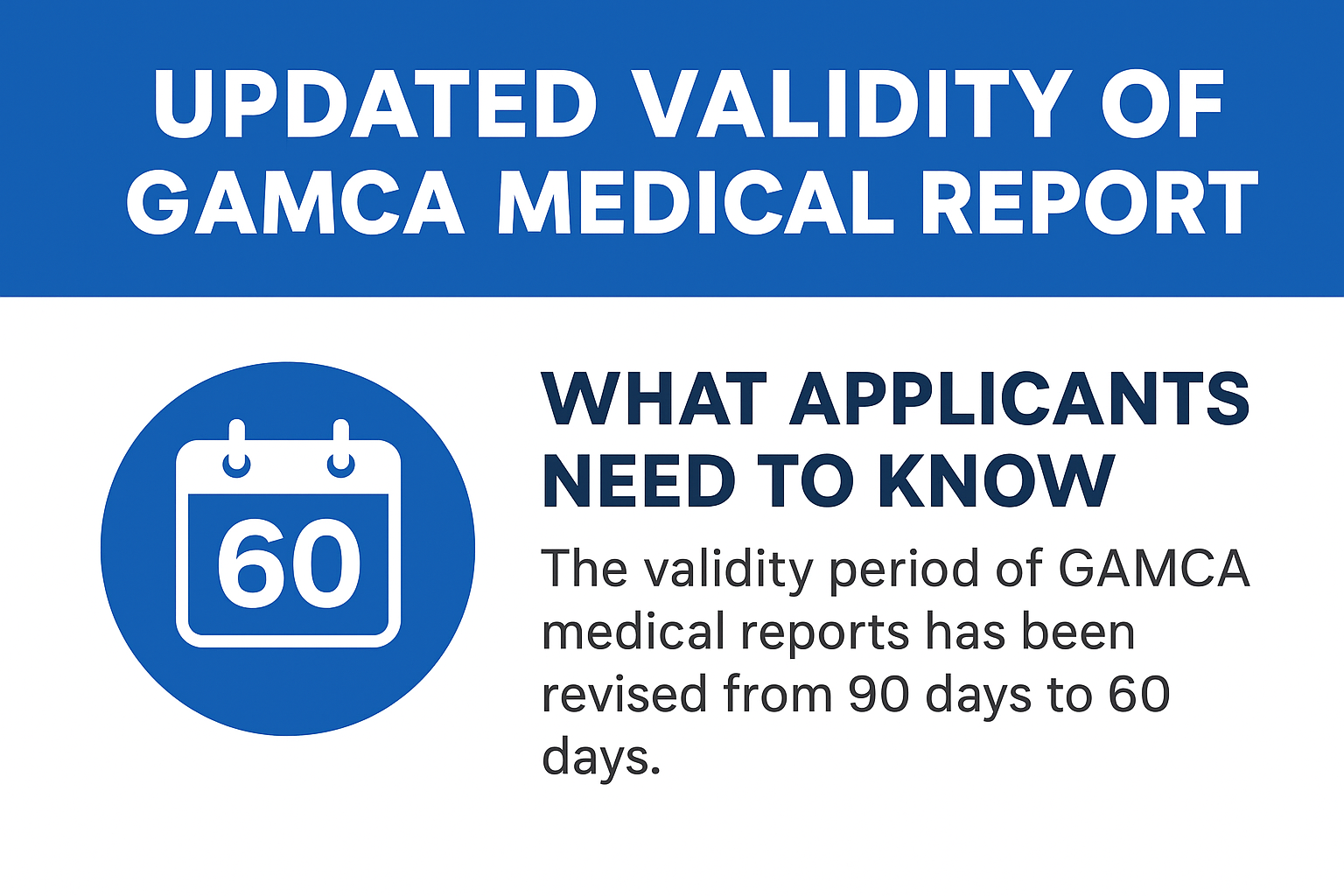
- Validity: GAMCA medical reports are valid for 90 days (or sometimes 60 days) from the issue date.
Specific Requirements for Children:
- Age Exemption: In most GCC countries, children under 12 years of age are generally not required to undergo the full GAMCA medical test.
- Partial Checks: However, particularly if they are coming for long-term residency or school, they might still need to present confirmation of vaccines or go through basic health examinations. These may consist of weight, height, and immunisation history.
- Older Children/Teenagers: Depending on the rules of the host nation, adolescents or youngsters 12 years of age and up may have to have specific medical exams. Although they might not be as comprehensive as those for adults, they might nevertheless include basic health examinations and, in cases of high risk, tuberculosis screening.
- Documentation for Children: Parents should bring the child’s original passport, passport-sized photos, and visa application documents. Up-to-date health records, including vaccination certificates, are important.
- Special Cases: If a child has a known medical condition, even if under the age limit, additional medical documentation or tests might be requested.
Special Considerations for Women (including Pregnancy):
- Reproductive Health: Women may undergo additional tests related to reproductive health, including evaluations for sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and gynaecological exams.
- Pregnancy: Because of the risk to the fetus, pregnant women are often exempt from chest X-rays. However, this exemption usually requires a NOC (No Objection Certificate) from the applicable embassy (such as the Saudi Embassy). This typically entails sending in ultrasound data and a report from a physician. Pregnant women may only require blood tests, urine tests, and an eye examination in place of X-rays. Avoid scheduling an appointment during the first trimester and let the medical centre know if you are pregnant.
Policies might alter and vary, therefore, it’s important to always confirm the latest and specific rules with the GCC country’s embassy or consulate before applying.